5 March 2025
Differences between hiring EU and non-EU employees in Spain
Hiring EU and non-EU employees in Spain involves distinct processes and regulatory requirements that can significantly impact how businesses expand their workforce. Understanding these differences is essential for ensuring compliance with Spanish labour laws, tax obligations, and immigration policies.
While EU employees benefit from streamlined procedures thanks to free movement regulations, hiring non-EU employees typically requires more extensive documentation, including work permits and visas.
In this article, we’ll explore the key distinctions between hiring EU and non-EU employees in Spain, from work permits to compliance requirements.
Hiring EU employees in Spain: Simplified process
One of the main advantages of hiring EU/EEA/Swiss citizens is their right to work in Spain without needing a visa or work permit. Employers only need to ensure that these employees register for a foreigner’s identification number (NIE) and are properly enrolled in Spain’s social security system.
This streamlined process makes it easier to onboard EU employees quickly and focus on integrating them into the workforce.
From a tax perspective, employers must withhold personal income tax (IRPF) and contribute to social security on behalf of their EU employees. While these obligations apply to all employees, the absence of visa sponsorship and additional immigration paperwork simplifies compliance. As a result, businesses can reduce administrative burdens and potential delays, making EU employees a preferred choice for many international employers in Spain.
Hiring non-EU employees in Spain: Work permits and visa requirements
In contrast, hiring non-EU employees involves navigating Spain’s work visa requirements. Employers must sponsor their prospective employees’ work permits and handle the associated legal procedures.
The type of work permit needed depends on the employee’s role and qualifications. Common options include the Highly Qualified Professional Visa for skilled workers and the General Work Visa for standard positions. Additionally, the Digital Nomad Visa is gaining popularity for remote workers.
The process for obtaining work permits can be time-consuming, often requiring proof that no suitable EU candidate is available for the role. Employers must also provide detailed employment contracts, submit the necessary documentation to Spanish authorities, and wait for approvals before the employee can begin working. These additional steps make hiring non-EU employees more complex, but they are critical for maintaining compliance and avoiding legal penalties.
Key differences between hiring EU and non-EU employees
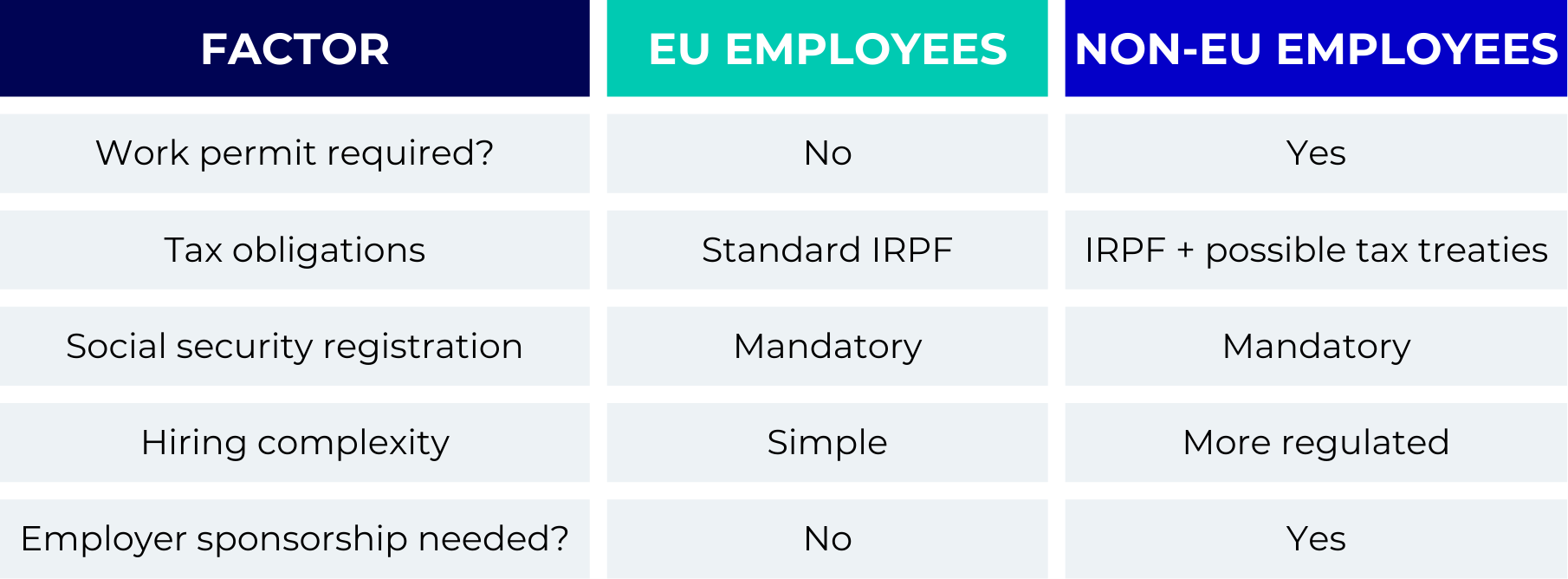
Compliance considerations for international employers
Taxation, employment contracts, and social security obligations differ significantly between EU and non-EU employees. Non-EU employees often have additional tax considerations, such as potential double taxation issues, which may require careful planning and consultation with tax advisors.
Employment contracts for non-EU workers must also meet the specific criteria required for work permits, while EU employee contracts typically follow standard Spanish labour law.
Employers must also navigate different social security contributions. While both EU and non-EU employees need to be registered with Spanish social security, non-EU workers may require additional documentation to ensure compliance. Understanding these differences helps businesses stay compliant and avoid costly mistakes when hiring international talent.
How an Employer of Record simplifies hiring in Spain
A Spanish Employer of Record (EOR) offers a straightforward solution for businesses hiring in Spain. By acting as the local legal employer, an EOR handles all compliance-related tasks, including payroll processing, tax withholding, and social security contributions.
For non-EU employees, an EOR can also manage work permit sponsorship and renewals, ensuring that all legal requirements are met without the need for the business to establish a local entity.
For instance, a U.S.-based technology firm wanted to hire a software engineer from Brazil to join their remote team in Spain. However, as a non-EU national, the new hire required a work visa and a compliant employment setup. Instead of managing Spain’s complex visa requirements and establishing a local legal entity, the company partnered with an Employer of Record.
The EOR managed the work permit application, handled local payroll and tax compliance, and ensured the employment contract met all Spanish labour law standards. This allowed the company to quickly onboard the engineer and focus on project delivery, while the EOR handled the administrative and legal complexities.
An EOR still provides valuable support for businesses hiring EU employees by ensuring compliance with Spanish labour laws, handling payroll deductions, and offering guidance on employment contracts. In both cases, the EOR reduces administrative burdens, simplifies the onboarding process, and helps businesses focus on growth rather than navigating complex regulations.
Hire both EU and non-EU employees easily
Hiring EU employees in Spain offers a straightforward path thanks to free movement rules, while hiring non-EU employees involves handling work permits, visas, and additional compliance steps. Understanding these key differences and ensuring proper payroll and tax compliance are essential for any business expanding into Spain.
Employers looking to streamline the process and ensure full compliance can benefit greatly from partnering with an Employer of Record. Contact us today to learn how we simplify hiring and workforce management, allowing businesses to hire EU and non-EU employees in Spain confidently and without the complexities of establishing a legal entity.
